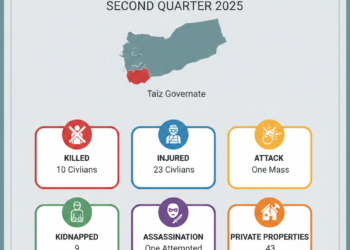
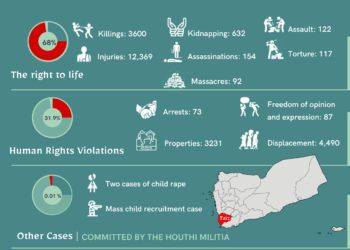
Armenian Genocide, campaign of deportationand mass killing conducted against the Armenian subjects of the Ottoman Empire by the Young Turk government during World War I (1914–18). Armenians charge that the campaign was a deliberate attempt to destroy the Armenian people and, thus, an act of genocide. The Turkish government has resisted calls to recognize it as such, contending that, although atrocities took place, there was no official policy of extermination implemented against the Armenian people as a group.
Armenians In Eastern Anatolia
For centuries the great mountain plateau of Eastern Anatolia—in present-day eastern Turkey—was inhabited primarily by Christian Armenians who shared the area with Muslim Kurds. In antiquity and the Middle Ages the area was ruled by a succession of Armenian dynasties, although it often faced incursions by outside powers. Armenian political independence was largely brought to an end by a wave of invasions and migrations by Turkic-speaking peoples beginning in the 11th century, and in the 15th and 16th centuries the region was secured by the Ottoman Turks and integrated into the vast Ottoman Empire. Armenians retained a strong sense of communal identity, however, embodied in the Armenian language and the Armenian Church. That sense of distinctiveness was fostered by the Ottoman millet system, which accorded non-Muslim minorities significant administrative and social autonomy.
At the beginning of the 20th century, there were about 2.5 million Armenians living in the Ottoman Empire, mostly concentrated in the six provinces of Eastern Anatolia. A significant number of Armenians also lived beyond the eastern border of the Ottoman Empire, in territory held by Russia. In Eastern Anatolia Armenians lived intermixed with the dominant Kurdish nomads. Armenians did not constitute a majority in any of the regions in which they lived, although they often resided in homogeneous villages and neighborhoods within towns and cities.
Life for Armenian villagers and townspeople in the Ottoman Empire was difficult and unpredictable, and they often received harsh treatment from the dominant Kurdish nomads. Because local courts and judges often favoured Muslims, Armenians had little recourse when they were the victims of violence or when their land, livestock, or property was taken from them.
The great majority of Armenians were poor peasants, but a few found success as merchants and artisans. Armenians’ involvement in international trade led in the 17th and 18th centuries to the establishment of significant Armenian settlements in Istanbul and other Ottoman port cities and as far away as India and Europe. Although Ottoman society was dominated by Muslims, a small number of Armenian families were able to attain prominent positions in banking, commerce, and government. For several generations in the 18th and 19th centuries, for example, the chief architects of the Ottoman court were in the Armenian Balian family. The prominence and influence of the well-educated and cosmopolitanArmenian elite had a drawback, however, in that it became a source of resentment and suspicion among Muslims. In the 19th century Armenians struggled against the perception that they were a foreign element within the Ottoman Empire and that they would eventually betray it to form their own independent state.
Young Armenian activists, many of them from Russian Caucasia, sought to protect their compatriots by agitating for an independent state. They formed two revolutionary parties called Hënchak (“Bell”) and Dashnaktsutyun (“Federation”) in 1887 and 1890. Neither one gained wide support among Armenians in Eastern Anatolia, who largely remained loyal and hoped instead that sympathizers in Christian Europe would pressure the Ottoman Empire to implement new reforms and protections for Armenians. The activities of the Armenian revolutionaries, however, did stoke fear and anxiety among the Muslims.

Anti-Armenian feelings erupted into mass violence several times in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. When, in 1894, the Armenians in the Sasun region refused to pay an oppressive tax, Ottoman troops and Kurdish tribesmen killed thousands of Armenians in the region. Another series of mass killings began in the fall of 1895, when Ottoman authorities’ suppression of an Armenian demonstration in Istanbul became a massacre. In all, hundreds of thousands of Armenians were killed in massacres between 1894 and 1896, which later came to be known as the Hamidian massacres. Some 20,000 more Armenians were killed in urban riots and pogroms in Adana and Hadjin in 1909.
In 1908 a small group of Ottoman revolutionaries—the Committee of Union and Progress (CUP), popularly referred to as the “Young Turks”—came to power. Armenians welcomed the restoration of the Ottoman constitution, and the promise of elections led Armenians and other non-Turks within the empire to cooperate with the new political order. Over time, however, the ambitions of the Young Turks became more militant, less tolerant of non-Turks, and increasingly suspicious of their Armenian subjects, whom they imagined were collaboratingwith foreign powers. Increasingly authoritarian, the Young Turks consolidated power and sidelined their more-liberal opponents, and in January 1913 the most-militant members of the party, Enver Paşa and Talat Paşa, came to power in a coup d’état.
Antipathy toward Christians increased when the Ottoman Empire suffered a humiliating defeat in the First Balkan War (1912–13), resulting in the loss of nearly all its remaining territory in Europe. Young Turk leaders blamed the defeat on the treachery of Balkan Christians. Furthermore, the conflict sent hundreds of thousands of Muslim refugees streaming eastward into Anatolia, intensifying conflict between Muslims and Christian peasants over land.
Fearful Armenians capitalized on the Ottoman defeat to press for reforms, appealing to the European powers to force the Young Turks to accept a degree of autonomy in the Armenian provinces. In 1914 the European powers imposed a major reform on the Ottomans that required supervision by inspectors in the east. The Young Turks took that arrangement as further proof of the Armenians’ collusion with Europe to undermine the sovereignty of the Ottoman Empire.
As World War I began in the summer of 1914, the Young Turks joined the Central Powers (Germany and Austro-Hungary) against the Triple Entente (Great Britain, France, and Russia). Because Armenians and Assyrians lived along the Russian-Ottoman front, both the Russians and the Ottomans attempted to recruit the local Christians in their campaigns against their enemies. The Young Turks proposed to the Dashnaktsutyun, by then the leading Armenian political party, that it convince Russian Armenians as well as those in Ottoman lands to fight for the Ottoman Empire. The Dashnaks replied that Armenian Russian and Ottoman subjects would remain loyal to their respective empires. That was seen by powerful Young Turks as an act of treachery.Armenians in the Ottoman Empire fought alongside the Ottomans, while Armenian volunteer units made up of Russian subjects fought on the Russian side. In the areas where Ottoman and Russian troops faced each other, there were massacres of both Christians and Muslims.
Genocide
In January 1915 Enver Paşa attempted to push back the Russians at the battle of Sarıkamış, only to suffer the worst Ottoman defeat of the war. Although poor generalship and harsh conditions were the main reasons for the loss, the Young Turk government sought to shift the blame to Armenian treachery. Armenian soldiers and other non-Muslims in the army were demobilized and transferred into labour battalions. The disarmed Armenian soldiers were then systematically murdered by Ottoman troops, the first victims of what would become genocide. About the same time, irregular forces began to carry out mass killings in Armenian villages near the Russian border.
Armenian resistance, when it occurred, provided the authorities with a pretext for employing harsher measures. In April 1915 Armenians in Van barricaded themselves in the city’s Armenian neighborhood and fought back against Ottoman troops, On April 24, 1915, citing Van and several other episodes of Armenian resistance, Talat Paşa ordered the arrest of approximately 250 Armenian intellectuals and politicians in Istanbul, including several deputies to the Ottoman Parliament. Most of the men who were arrested were killed in the months that followed.
Soon after the defeat at Sarıkamış, the Ottoman government began to deport Armenians from Eastern Anatolia on the grounds that their presence near the front lines posed a threat to national security. In May the Ottoman Parliament passed legislation formally authorizing the deportation. Throughout summer and autumn of 1915, Armenian civilians were removed from their homes and marched through the valleys and mountains of Eastern Anatolia toward desert concentration camps. The deportation, which was overseen by civil and military officials, was accompanied by a systematic campaign of mass murder carried out by irregular forces as well as by local Kurds and Circassians. Survivors who reached the deserts of Syria languished in concentration camps, many starved to death, and massacres continued into 1916. Conservative estimates have calculated that some 600,000 to more than 1,000,000 Armenians were slaughtered or died on the marches. The events of 1915–16 were witnessed by a number of foreign journalists, missionaries, diplomats, and military officers who sent reports home about death marches and killing fields.
Causes And Consequences Of The Genocide
The Armenian Genocide laid the ground for the more-homogeneous nation-state that eventually became the Republic of Turkey. By the end of the war, more than 90 percent of the Armenians in the Ottoman Empire were gone, and many traces of their former presence had been erased. The deserted homes and property of the Armenians in Eastern Anatolia were given to Muslim refugees, and surviving women and children were often forced to give up their Armenian identities and convert to Islam. Tens of thousands of orphans, however, found some refuge in the protection of foreign missionaries.
-
 An Armenian refugee camp in the Caucasus, 1920.George Grantham Bain Collection/Library of Congress, Washington, D.C. (digital file no. 27082)
An Armenian refugee camp in the Caucasus, 1920.George Grantham Bain Collection/Library of Congress, Washington, D.C. (digital file no. 27082)
The Armenian Genocide had both short- and long-term causes. Although the expulsion and murder of hundreds of thousands of Armenians in 1915–16 was an immediate response to the crisis of World War I and not the result of a long-held plan to eliminate the Armenian people, its deeper causes go back to Muslims’ resentment of Armenians’ economic and political successes—a reversal of traditional Ottoman social hierarchies that had Muslims superior to non-Muslims—and to a growing sense on the part of Young Turk leaders and ordinary Muslims that Armenians were an alien and dangerous element within their society.
Turkey has steadily refused to recognize that the events of 1915–16 constitute a genocide, even though most historians have concluded that the deportations and massacres do fit the definition of genocide—the intentional killing of an ethnic or religious group. While the Turkish government and allied scholars have admitted that deportations took place, they maintain that the Armenians were a rebellious element that had to be pacified during a national security crisis. They acknowledge that some killing took place, but they contend that it was not initiated or directed by the government. Major countries—including the United States, Israel, and Great Britain—have also declined to call the events a genocide, in order to avoid harming their relations with Turkey. In 2015 government officials in Turkey offered condolences to the Armenian victims, but Armenians remained committed to having the killings during World War I recognized as a genocide